According to the news from the EU parliament, the EU parliament approved new regulations for the design, production, and waste management of all types of batteries sold in the EU on June 14th, 2023. The EU New Battery Regulation concerning batteries and waste batteries considers technological developments and future challenges in the sector. It will cover the entire battery life cycle, from design to end-of-life.
Background of EU New Battery Regulation
The European Commission proposed that Europe will achieve "carbon neutrality" by 2050 to respond to global climate change and promote green and low-carbon economic development. To achieve this goal, the European Commission focused on the battery industry. It implemented a series of measures, including a three-year assessment of the "EU Battery Directive" launched in 2017 and the "Strategic Action Plan on Batteries" released in 2018. In the following two years, the "European Green Deal" and "Circular Economy Action Plan" were successively promulgated, reaffirming the importance of the healthy and sustainable development of the battery industry.
On December 10, 2020, the European Commission announced the new "EU Battery Regulation" aimed at promoting the sustainable development of the battery. The regulation applies to portable, automotive, industrial, and power batteries. It contains 13 chapters, 79 clauses, and 14 annexes. The European Commission will launch more than 30 subsidiary regulations to support the implementation of the regulation. The regulation took effect on January 1, 2022. This new regulation will help Europe establish a sustainable, competitive, innovative battery value chain.
Legislative Process of EU New Battery Regulation
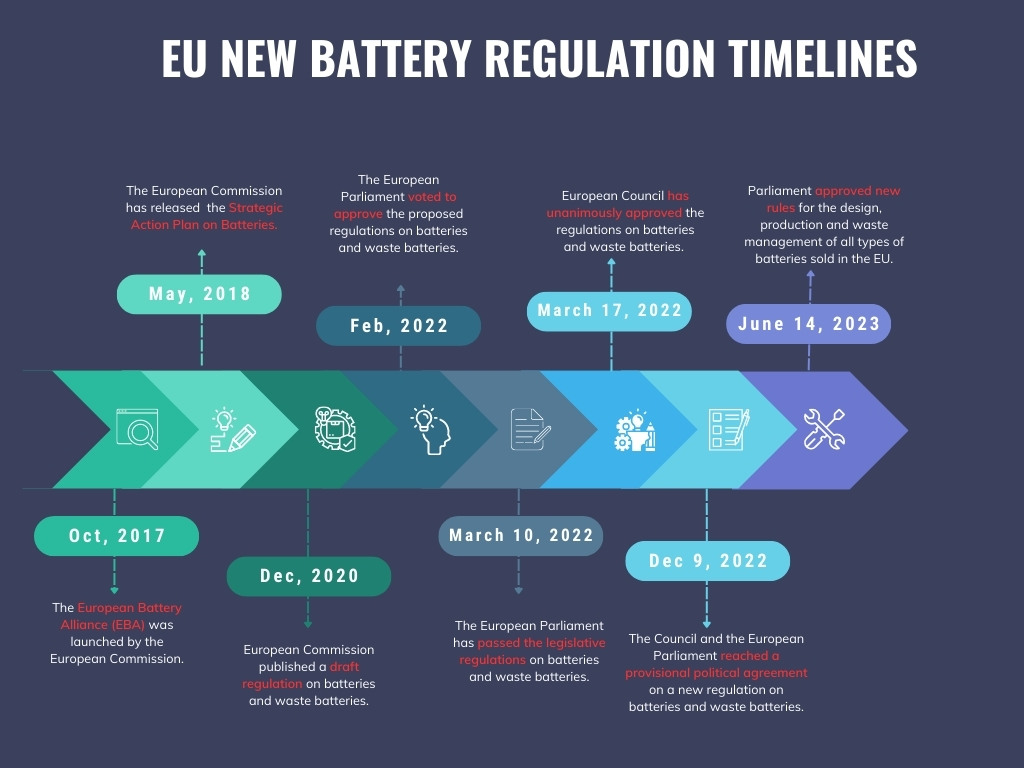
Battery development and production are strategic imperatives for Europe in the context
of the clean energy transition. A series of legislative works have been done within Europe Parliament and Europe Council to modernize the EU's battery legislative framework.
✱In Oct 2017, the European Battery Alliance (EBA) was launched by the European Commission, member countries, industry, and the scientific community.
✱In May 2018, the European Commission released the Strategic Action Plan on batteries. The measures of this plan cover a range of areas, including raw materials extraction, sourcing and processing, battery materials, battery production, battery systems, reuse, and recycling.
✱In Dec 2020, the European Parliament passed the legislative regulations on batteries and waste batteries. The regulation proposes mandatory requirements on sustainability, including carbon footprint rules, minimum recycling content, performance, and durability standards, safety and labeling for marketing and use of batteries, and requirements for end-of-life management.
✱In Feb 2022, the European Parliament voted to approve the proposed batteries and waste batteries regulations. Stricter requirements and higher targets have been set regarding sustainability and recycling requirements.
✱On March 10, 2022, the European Parliament passed the legislative regulations on batteries and waste batteries. Stricter requirements have been proposed in several areas, including battery scope management, data and labeling management, battery performance requirements, supply chain due diligence, and carbon footprint.
✱On March 17, 2022, the European Council unanimously approved the batteries and waste batteries regulations.
✱On Dec 9, 2022, the Council and the European Parliament reached a provisional political agreement on new batteries and waste batteries regulations.
✱On June 14, 2023, the Parliament approved new rules for the design, production, and waste management of all types of batteries sold in the EU.
What Is New About EU New Battery Regulation?
✸Battery companies Provide carbon footprint declaration and labeling
A compulsory carbon footprint declaration and label for electric vehicles (EV) batteries, light means of transport (LMT) batteries (e.g., for electric scooters and bikes), and rechargeable industrial batteries with a capacity above 2kWh; Companies must collect and calculate carbon emissions data for batteries sold to the EU in each lifecycle stage, including upstream raw materials, product manufacturing, transportation, disposal, and recycling, according to relevant standards.
✸Minimum levels of materials recovered from waste batteries
This refers to the percentage of end-of-life batteries that can be recycled, covering all types of batteries. The European Commission states that these regulations will ensure that valuable materials are recovered at the end of their useful life and are reintroduced into the economy through progressively stricter recycling efficiency and material recovery targets over time.
| 5. Recycling efficiencies and recovery of materials | Lithium-ion batteries and Co, Ni, Li, Cu:
Recycling efficiency lithium-ion batteries: 65% by 2025 Material recovery rates for Co, Ni, Li, Cu: resp. 90%, 90%, 35% and 90% in 2025
Lead-acid batteries and lead: Recycling efficiency lead-acid batteries: 75% by 2025 Material recovery for lead: 90% in 2025 |
Lithium-ion batteries and Co, Ni, Li, Cu:
Recycling efficiency lithium-ion batteries: 70% by 2030 Material recovery rates for Co, Ni, Li, Cu: resp. 95%, 95%, 70% and 95% in 2030
Lead-acid batteries and lead: Recycling efficiency lead-acid batteries: 80% by 2030 Material recovery for lead: 95% by 2030
|
/ |
✸A digital battery passport for LMT batteries, industrial batteries with a capacity above 2 kWh, and EV batteries
The new Battery Regulation introduces requirements for battery labeling and information disclosure, as well as requirements for battery digital passports and QR codes. The information that needs to be disclosed includes product capacity, performance, use, chemical composition, recyclable contents, and other information.
The Battery Regulation requires that within 48 months of the regulation, the Commission shall establish a universal information exchange system, and each electric vehicle battery placed on the market shall have an electronic record, i.e., a "battery passport."
What Does EU New Battery Regulation Mean as a Battery Manufacturer?
Battery manufacturers, including Chinese battery companies, will face stricter environmental and due diligence requirements if they want to sell batteries in the European market after implementing the new EU Battery Regulation. These requirements include but are not limited to providing battery carbon footprint declaration and labeling, setting minimum recycling rates and material recovery targets, and providing battery QR codes and digital passports. In addition, the EU will rate the carbon footprint of battery companies and set a threshold in 2027, above which they will be unable to enter the EU market. Therefore, battery manufacturers need to establish sound carbon footprint mechanisms, actively participate in carbon market construction, and promote the development of carbon footprint management and emission reduction work to meet the EU's environmental and due diligence requirements.
Non-rechargeable Portable Batteries Will be Gradually Phased Out in 2023
The EU New Battery Regulation does not mandate a full phase-out of non-rechargeable portable batteries now. However, the EU New Battery Regulation includes measures to encourage rechargeable batteries and improve the environmental performance of batteries. For example, the Regulation requires that all batteries placed on the EU market meet certain sustainability criteria, including minimum performance and durability requirements. In addition, the Regulation mandates that batteries be labeled with information on their environmental impact, including their carbon footprint, to inform consumers and promote responsible battery use and disposal. While the Regulation does not currently call for a full phase-out of non-rechargeable batteries, it aims to improve the sustainability and environmental performance of all batteries placed on the EU market.
According to the EU New Battery Regulation, the non-rechargeable portable batteries will be assessed for the feasibility of phasing out in the EU market. Learn more from part of the EU New Battery Regulation.
“By 31 December 2030, the Commission shall assess the feasibility of measures to phase out the use of non-rechargeable portable batteries of general use and, to that end, submit a report to the European Parliament and to the Council and consider taking the appropriate measures, including the adoption of legislative proposals.”
| Measures | Option 2 - medium level of ambition | Option 3 - high level of ambition | Option 4 – very high level of ambition |
| 8. Non-rechargeable portable batteries | Technical parameters for performance and durability of portable primary batteries
|
Phase out of portable primary batteries of general use | Total phase out of primary batteries
|
“For Measure 8 on non-rechargeable portable batteries, the preferred option is Option 2, setting electrochemical performance and durability parameters to minimise the inefficient use of resources and energy. These parameters will also be taken up by the labelling requirements that are covered by Measure 12 to inform consumers’ batteries' performance. With regards to Options 3 and 4 the conclusion is that there is currently not sufficient evidence available to demonstrate the effectiveness and feasibility of a partial or complete phase out of non-rechargeable batteries. Producers and recyclers of non-rechargeable batteries are opposed to these two more ambitious options.”
Golden Opportunity for NiMH Rechargeable Battery
The recent EU New Battery Regulation, although not mandating a complete phase-out of non-rechargeable portable batteries, presents a golden opportunity for a NiMH rechargeable battery in the EU market. As the Regulation emphasizes the promotion of rechargeable batteries and enforces stringent sustainability criteria for all batteries entering the EU market, demand for eco-friendly, high-performance rechargeable batteries, such as NiMH rechargeable batteries, is expected to soar.
Furthermore, the impending phase-out of non-rechargeable batteries in the EU will create a significant market gap that NiMH rechargeable and other rechargeable batteries can capitalize on. Weijiang Power, as a professional NiMH battery factory in China, we can ensure that our rechargeable batteries meet the EU's performance, durability, and environmental standards. Weijiang Power provides a full range of customized NiMH battery services, like custom A NiMH battery, custom AA NiMH battery, custom AAA NiMH battery, custom C NiMH battery, custom D NiMH battery, custom 9V NiMH battery, custom F NiMH battery, and custom NiMH battery pack services. We are working hard to position ourselves as a preferred supplier in the European market with over 13 years of experience in providing OEM services to top NiMH battery brands in the EU market.
Weijiang Power can help our battery customers in the EU market secure a strong market position, establishing itself as a preferred supplier of rechargeable batteries in the European market and driving growth in the green energy sector.
Other Types of Custom NiMH Battery




Custom AA NiMH Battery
Custom AAA NiMH Battery
Custom C NiMH Battery
Custom D NiMH Battery



Custom F NiMH Battery
Custom Sub C NiMH Battery
Custom A NiMH Battery
Custom NiMH Battery Pack
Post time: Jul-05-2023





